Decentralization vs Usability: Can We Find the Perfect Balance?
The widespread adoption of Web3 technology heavily depends on how the registration and login process is addressed in decentralized applications. In order to enhance user experience and facilitate adoption, different authentication methods have been developed. In this article, we explore the three main approaches:
Cryptography-Based Authentication
This approach has been widely used in the context of Web3, for example Metamask, and Trust Wallet. It requires users to generate a private key and an associated pair of public keys. These keys are used to sign transactions and demonstrate ownership of digital assets. While this approach is strong in terms of security and decentralization, it can be complex for non-technical users.
🔒 Cryptography-based: Users generate private and public keys to sign transactions and prove ownership.
Perks and Cons
Any loss can result in the loss of funds.
Key management and understanding of cryptography can present significant entry barriers.
Greater security and direct control of private keys.
Less reliance on third parties.
Passwordless Authentication
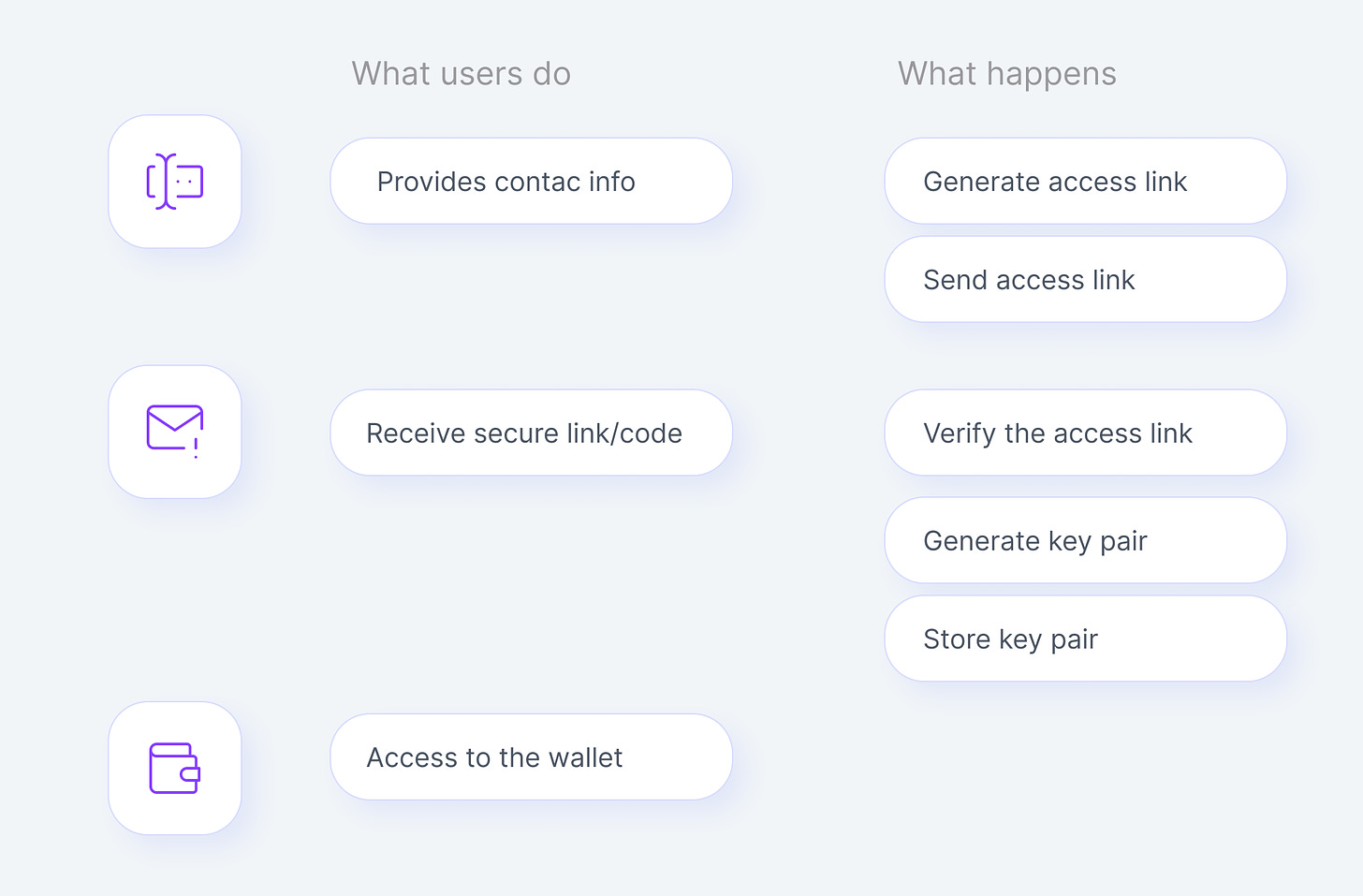
An emerging approach in Web3 that eliminates the need for traditional passwords, instead, methods such as secure access links sent via email are used. This approach aims to improve the authentication experience by removing the need to remember complex passwords and mitigating the security risks associated with passwords. This approach it’s used by Magic, Torus...
✉️ Passwordless: Users provide contact information and receive secure access links via email.
Perks and Cons
Greater convenience and simplicity for users.
Lower risk of weak or stolen passwords.
Dependency on an external provider to manage authentication.
Device-Based Authentication
Combines the security of cryptography-based authentication with the ease of use of dedicated devices. This approach provides a frictionless experience as users can access their accounts and sign transactions with just a few clicks on their device. Safe (previously Gnosis Safe), and Ledger are some examples.
📱 Device-based: Users effortlessly access their accounts and sign transactions with a few clicks on their trusted device
Perks and Cons
Higher security and control over private keys.
A familiar user interface for cryptocurrency wallet users.
Requires having a cryptographic wallet installed and configured on the device.
May limit accessibility for those without a wallet or unfamiliar with them.
Conclusion
Authentication is a key component in the successful adoption of Web3. It has evolved to adapt to user needs and improve the adoption of blockchain technology. However, it is important to consider the trade-off between decentralization and usability in the authentication process. Do users need to deeply understand the internal workings of blockchain technology, or do they simply need a seamless and accessible user experience?
Undoubtedly, deep understanding is not necessary; users only need to be able to use it and achieve their goals. However, continuing in this direction would undermine the fundamental aspect of blockchain decentralization. It is crucial to find a balance between decentralization and usability.
Furthermore, it is important to note that the authentication process is just the first step in the user's experience with Web3 technology. Once authenticated, users can engage in a wide range of activities such as purchasing NFTs, conducting transactions, or participating in DeFi.
The authentication process in Web3 has evolved to meet user needs and enhance the adoption of blockchain technology. However, user education in the form of interactive tutorials, explanatory videos, and detailed user guides will continue to be a crucial pillar for users to fully leverage its benefits. This education will enable a smoother transition to decentralized applications and maximize the potential of Web3.